Difference between revisions of "Document:Information for Voters"
(Created page with 'This document is intended to explain how to vote and how votes are counted in elections for the Delegate and Senate. Under the [[Con…') |
(→Single transferable vote) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This document is intended to explain how to vote and how votes are counted in elections for the [[Delegate of Taijitu|Delegate]] and [[Senate of Taijitu|Senate]]. Under the [[Constitution of Taijitu|Constitution]], the Delegate is elected by an instant run-off vote (IRV) and the Senate by the single transferable vote (STV). These systems | + | This document is intended to explain how to vote and how votes are counted in elections for the [[Delegate of Taijitu|Delegate]] and [[Senate of Taijitu|Senate]]. Under the [[Constitution of Taijitu|Constitution]], the Delegate is elected by an instant run-off vote (IRV) and the Senate by the single transferable vote (STV). These systems ensure majority-rule and proportional representation respectively. |
==How to vote== | ==How to vote== | ||
| − | Voting in both Delegate and Senate elections is the same. To vote, rank any number of candidates in order of preference. Ranking | + | Voting in both Delegate and Senate elections is the same. To vote, rank any number of candidates in order of preference, with 1 being the most preferred. Ranking as many candidates as possible will minimize the chance your vote is wasted and is highly encouraged, but you should not rank candidates who you do not want your vote being counted for under any circumstances. |
| + | |||
==Counting the votes== | ==Counting the votes== | ||
| + | ===Instant Runoff Voting=== | ||
Ballots in Delegate elections using IRV are counted as follows: | Ballots in Delegate elections using IRV are counted as follows: | ||
| − | #Each ballot is | + | #Each ballot is awarded to the candidate ranked highest on it. |
#If a single candidate has a majority, they are the winner and elected. | #If a single candidate has a majority, they are the winner and elected. | ||
| − | #If no candidate has a majority, the | + | #If no candidate has a majority, the one with the least votes is eliminated, and their ballots are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them. |
| − | # | + | #Steps 2 and 3 are repeated until a candidate wins a majority and is elected. |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Single transferable vote=== | ||
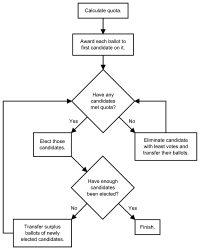
| + | [[Image:STV_flowchart.png|200px|right|thumb|A flowchart summarizing how votes are counted.]] | ||
Ballots in Senate elections using STV are counted as follows: | Ballots in Senate elections using STV are counted as follows: | ||
| − | #A quota | + | #A quota equal to V/(S+1)+1 rounded down, where V is the number of votes and S is the number of seats being elected, is calculated. |
| − | #Each | + | #Each ballot is awarded to the candidate ranked highest on it. |
| − | #If | + | #If any candidates meet the quota, they are elected, and the ballots they exceeded the quota by are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them. |
| − | #If no candidate meets the quota, the | + | #If no candidate meets the quota, the one with the least votes is eliminated, and their ballots are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them. |
| − | # | + | #Steps 3 and 4 are repeated until every seat has been filled. |
| + | The quota ensures that each Senator is elected by and represents a roughly equal number of voters, so that no group is either underrepresented or overrepresented. Transferring the ballots of eliminated candidates prevents a faction from splitting its vote, while transferring surplus ballots prevents a faction from concentrating its votes in a single candidates when they could elect more. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:17, 26 December 2011
This document is intended to explain how to vote and how votes are counted in elections for the Delegate and Senate. Under the Constitution, the Delegate is elected by an instant run-off vote (IRV) and the Senate by the single transferable vote (STV). These systems ensure majority-rule and proportional representation respectively.
Contents
[hide]How to vote
Voting in both Delegate and Senate elections is the same. To vote, rank any number of candidates in order of preference, with 1 being the most preferred. Ranking as many candidates as possible will minimize the chance your vote is wasted and is highly encouraged, but you should not rank candidates who you do not want your vote being counted for under any circumstances.
Counting the votes
Instant Runoff Voting
Ballots in Delegate elections using IRV are counted as follows:
- Each ballot is awarded to the candidate ranked highest on it.
- If a single candidate has a majority, they are the winner and elected.
- If no candidate has a majority, the one with the least votes is eliminated, and their ballots are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them.
- Steps 2 and 3 are repeated until a candidate wins a majority and is elected.
Single transferable vote
Ballots in Senate elections using STV are counted as follows:
- A quota equal to V/(S+1)+1 rounded down, where V is the number of votes and S is the number of seats being elected, is calculated.
- Each ballot is awarded to the candidate ranked highest on it.
- If any candidates meet the quota, they are elected, and the ballots they exceeded the quota by are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them.
- If no candidate meets the quota, the one with the least votes is eliminated, and their ballots are each transferred to the next choice ranked on them.
- Steps 3 and 4 are repeated until every seat has been filled.
The quota ensures that each Senator is elected by and represents a roughly equal number of voters, so that no group is either underrepresented or overrepresented. Transferring the ballots of eliminated candidates prevents a faction from splitting its vote, while transferring surplus ballots prevents a faction from concentrating its votes in a single candidates when they could elect more.